In Pictures
‘Like breathing poison’: Children in India’s Delhi hit hard by smog
The foul air severely impacts children, with devastating effects on their health and development.
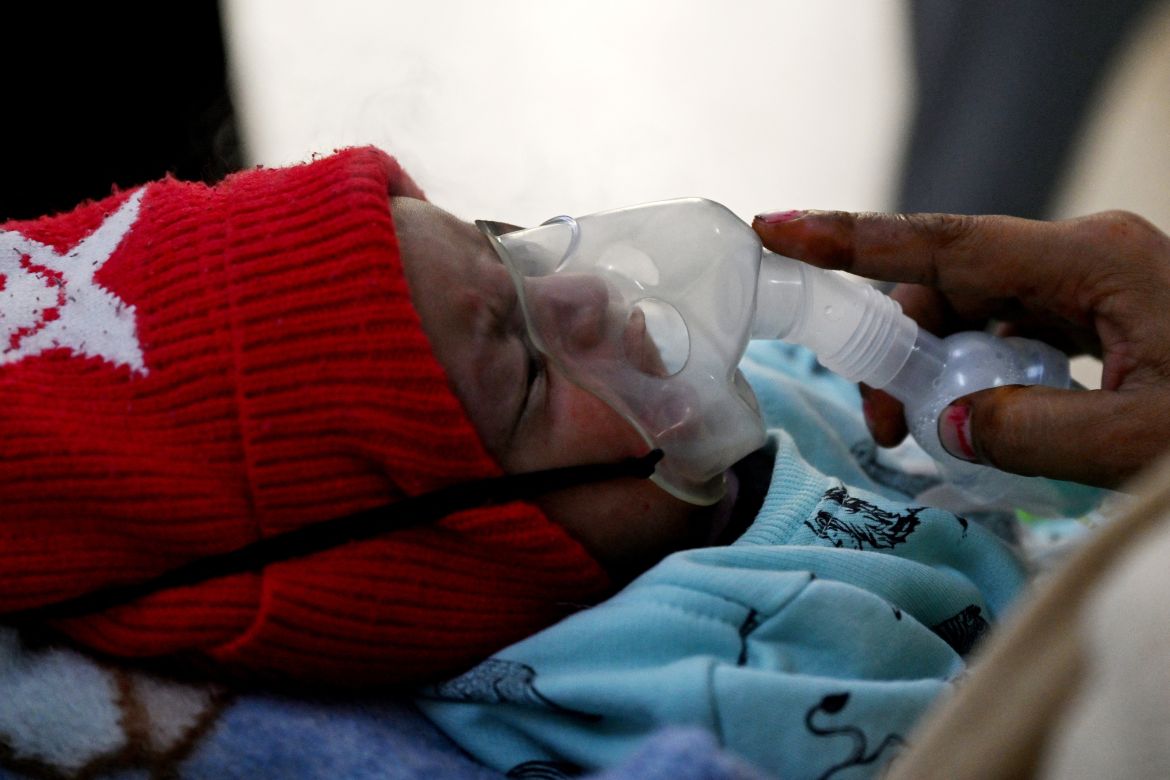

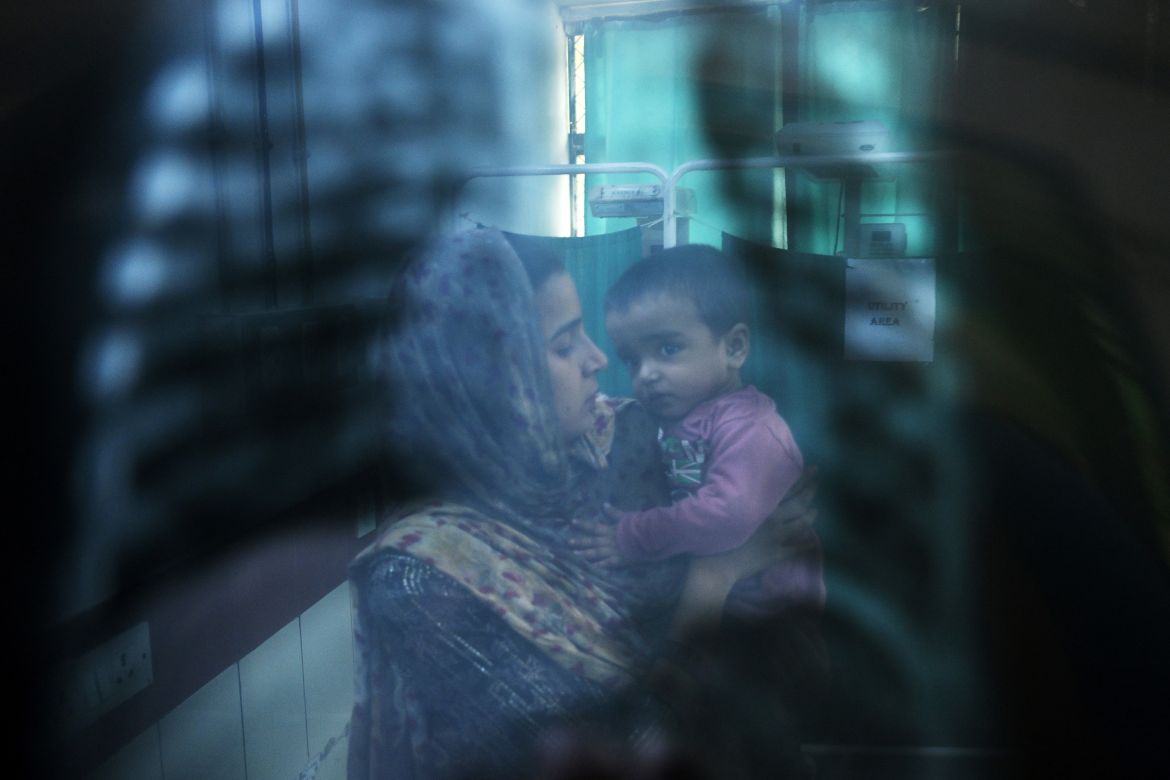
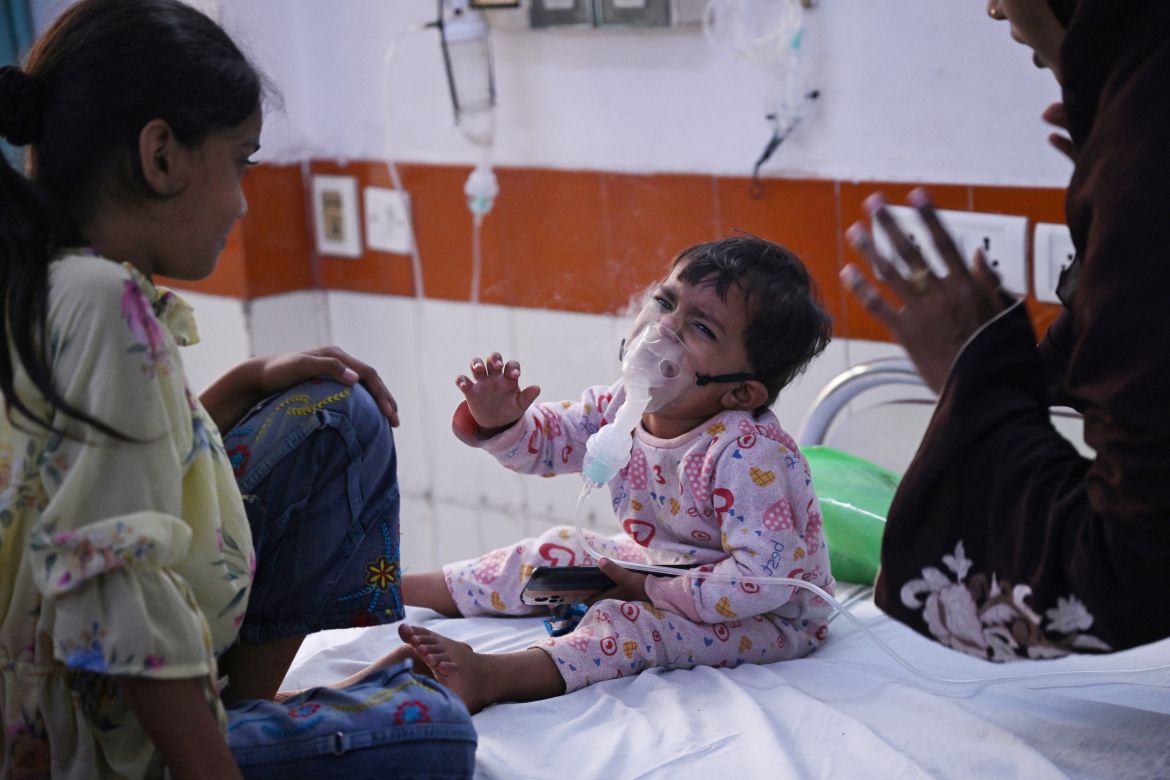
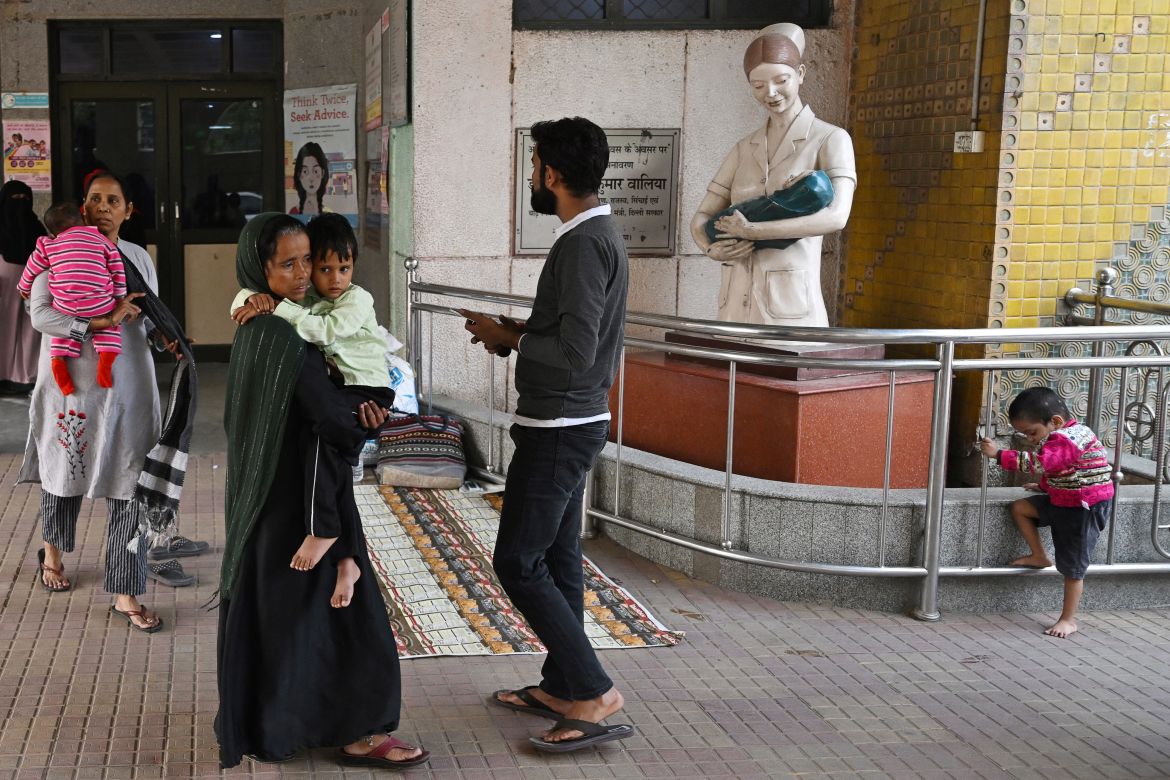
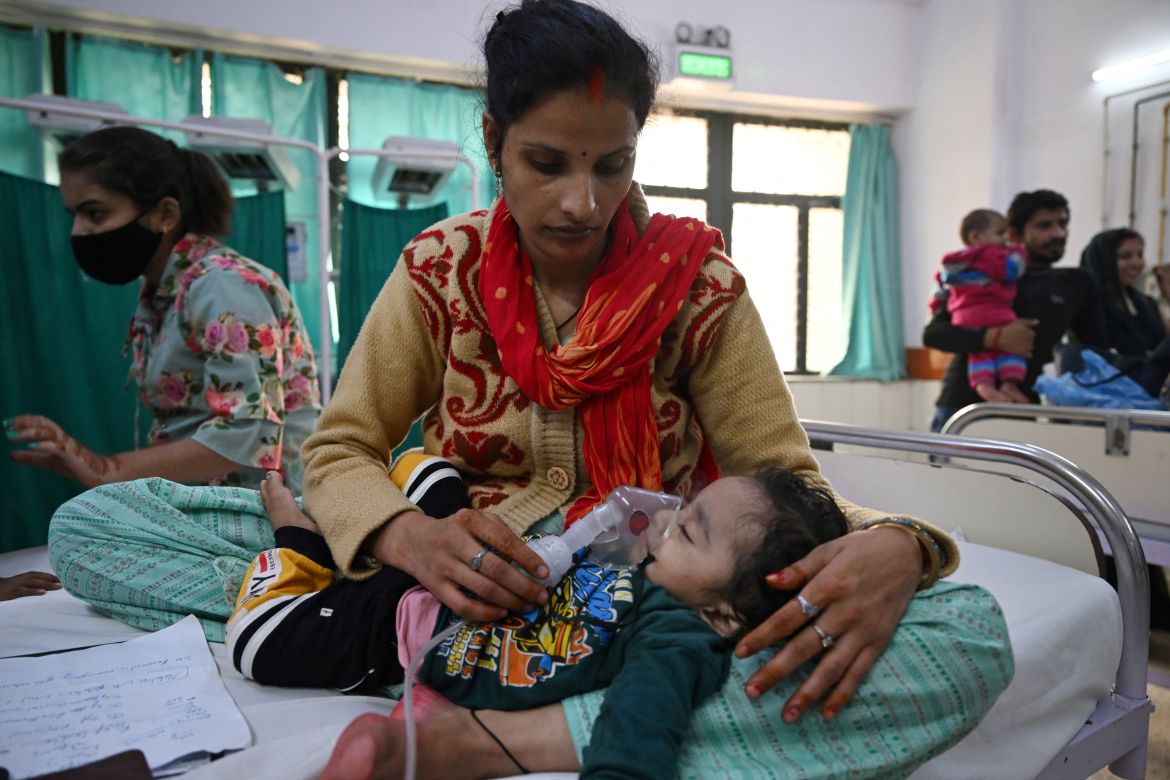
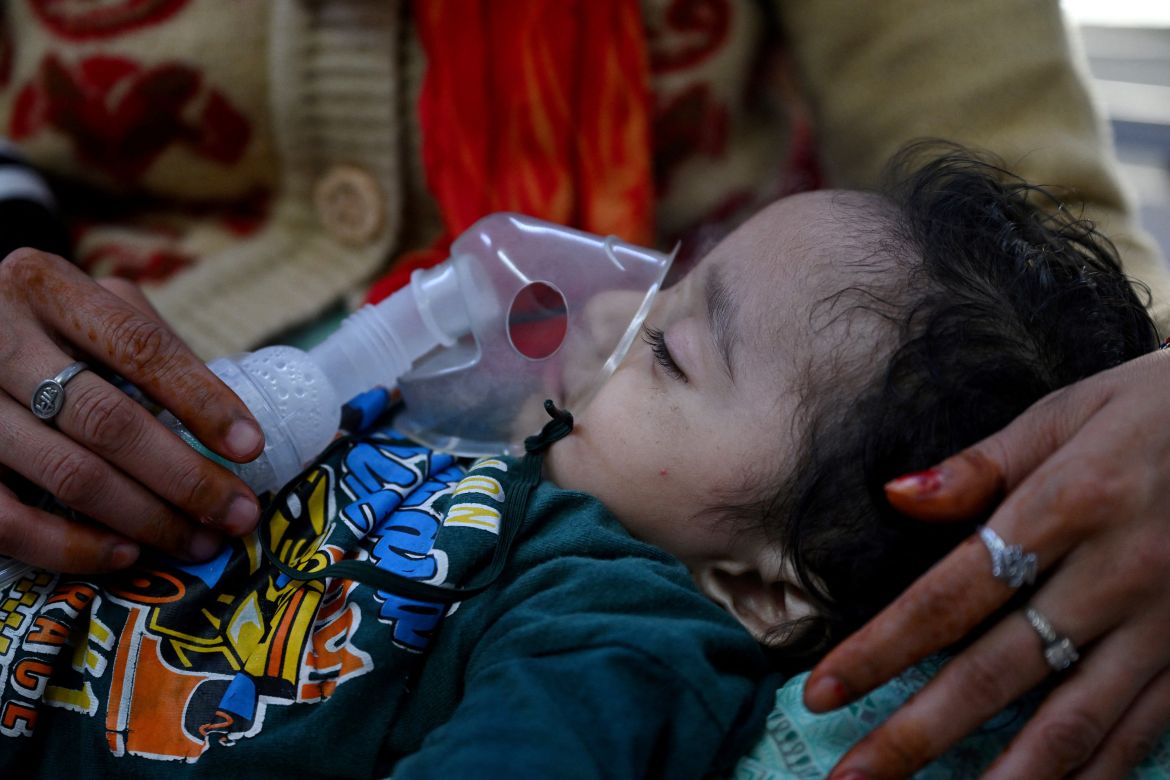
Crying in a hospital bed with a nebuliser mask on his tiny face, one-month-old Ayansh Tiwari has a thick, hacking cough. His doctors blame the acrid air that blights New Delhi every year.
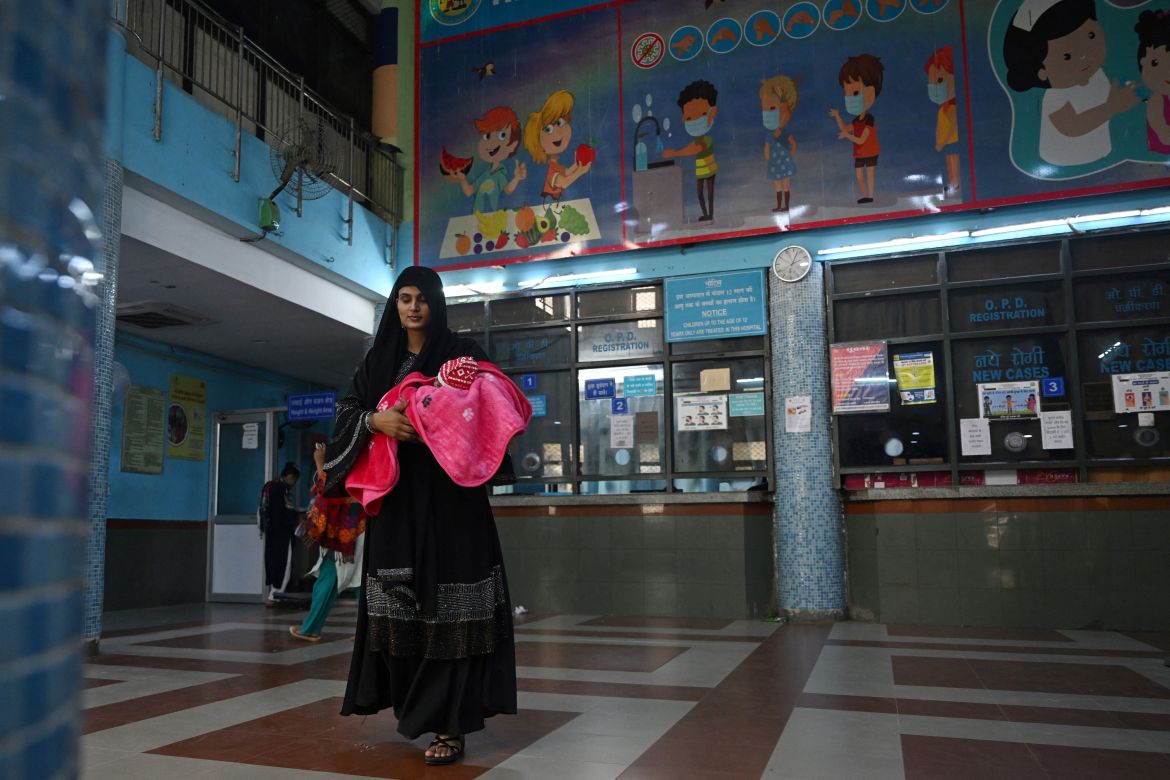
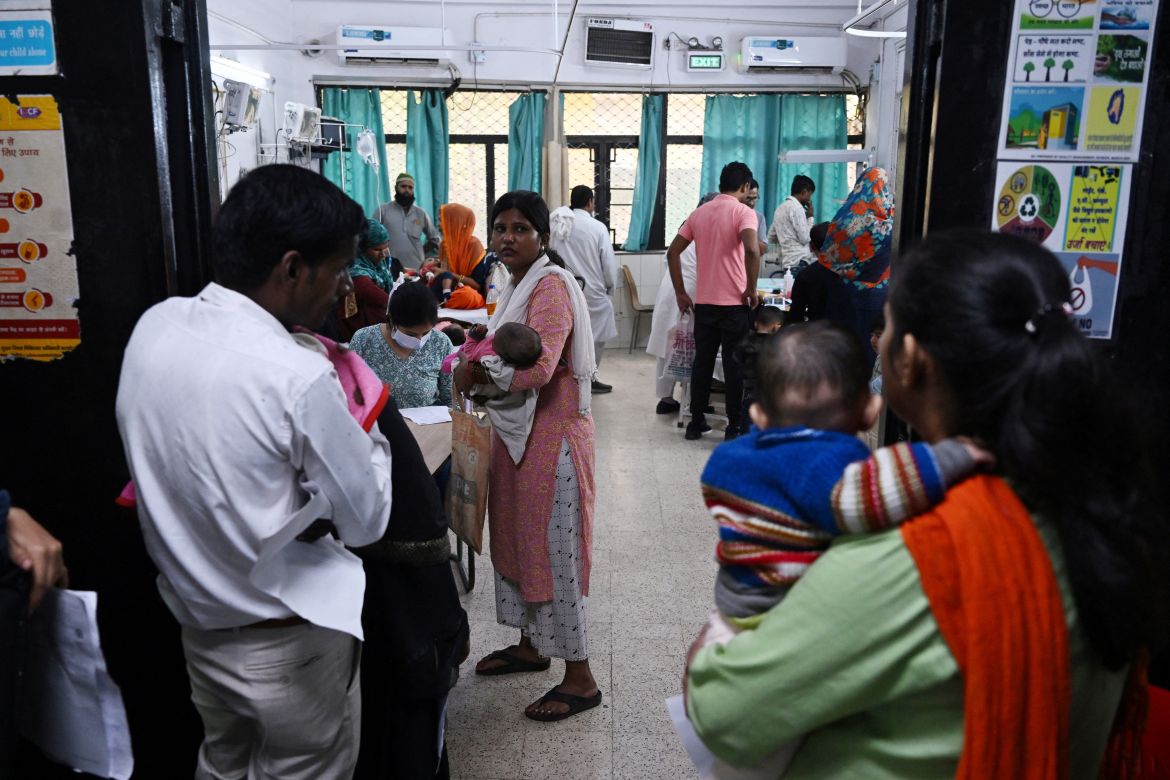
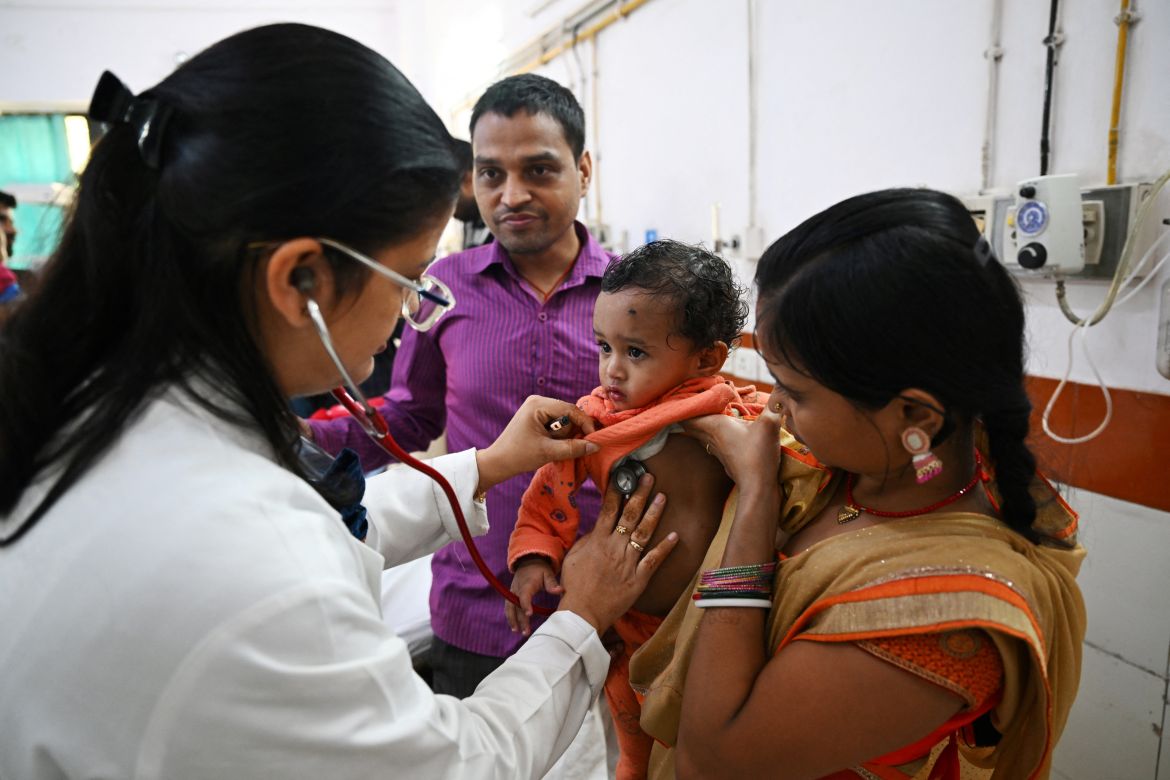
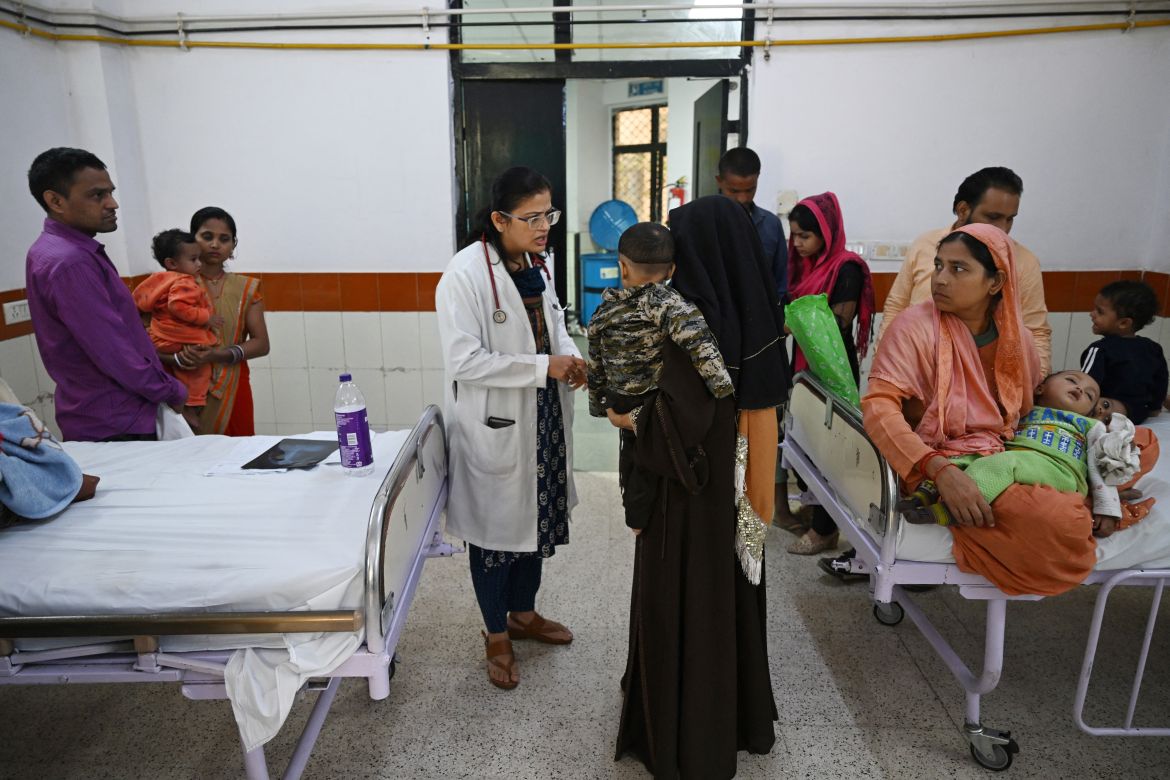
The spartan emergency room of the government-run Chacha Nehru Bal Chikitsalaya hospital in the Indian capital is crowded with children struggling to breathe. Many have asthma or pneumonia, conditions that spike as air pollution peaks each winter in the megacity of 30 million people.
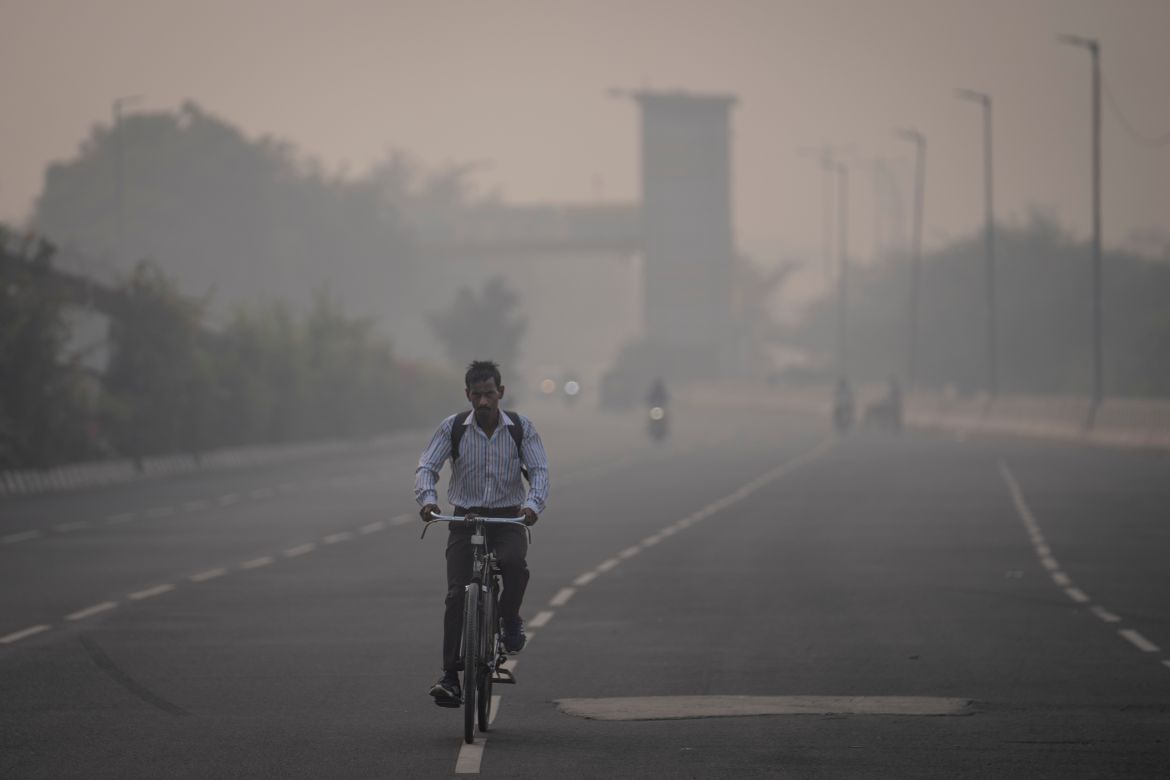
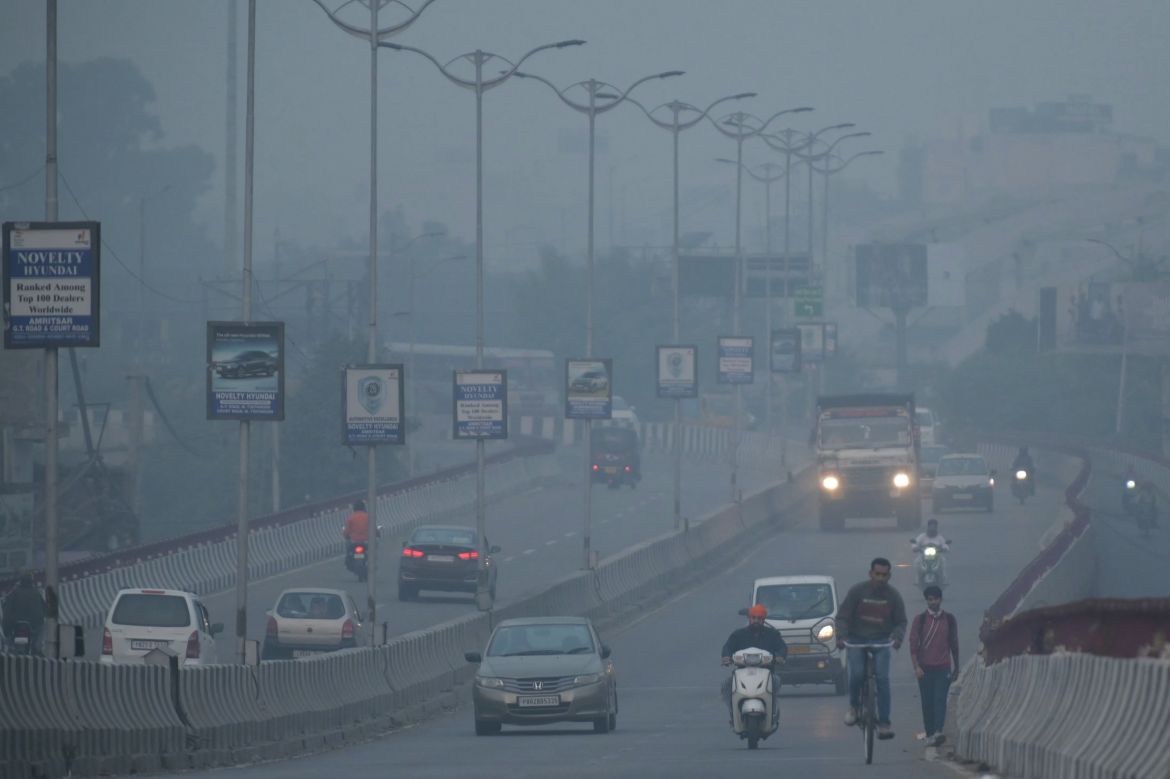
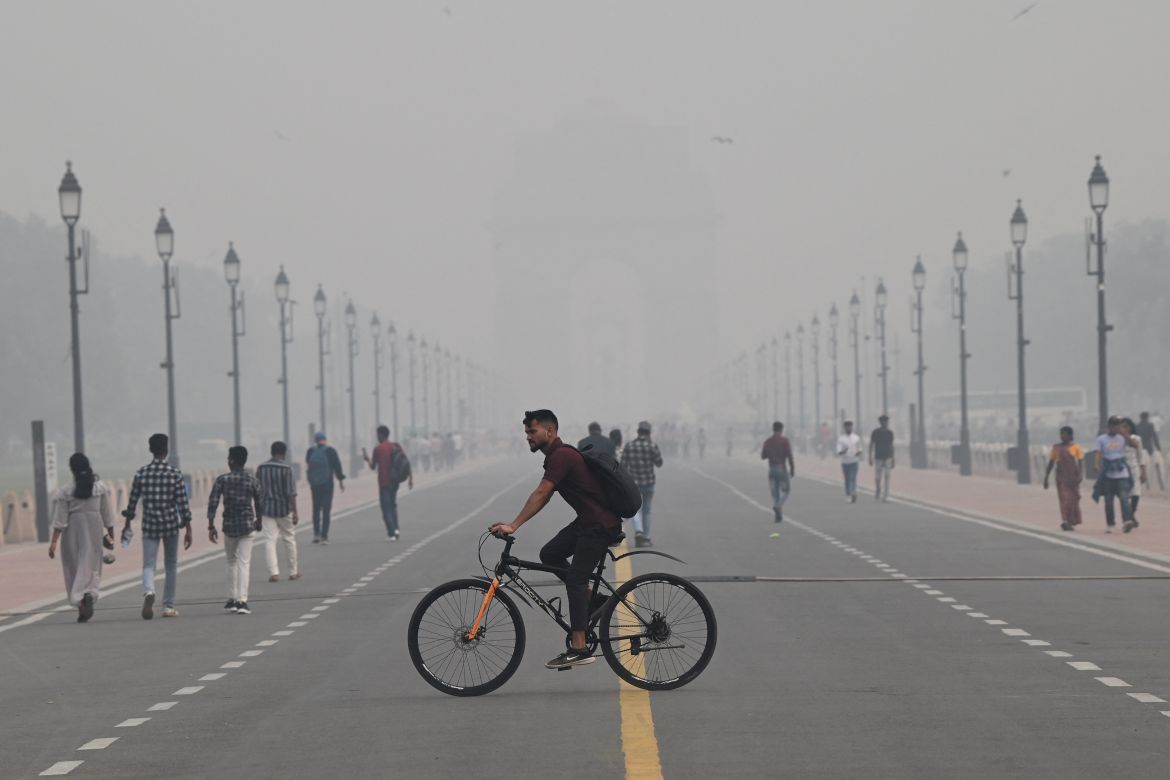
Delhi regularly ranks among the most polluted major cities on the planet, with a melange of factory and vehicle emissions exacerbated by seasonal agricultural fires.
“Wherever you see there is poisonous smog,” said Ayansh’s mother Julie Tiwari, 26, as she rocked the baby on her lap, attempting to calm him.
“I try to keep the doors and windows closed as much as possible. But it’s like breathing poison all the time. I feel so helpless,” she said, fighting back tears.
On Thursday, the level of PM2.5 particles – small enough to enter the bloodstream – topped 390 micrograms per cubic metre, according to monitoring firm IQAir. That’s more than 25 times the daily maximum recommended by the World Health Organization.
Government efforts have so far failed to solve the country’s air quality problem, and a study in the Lancet medical journal attributed 1.67 million premature deaths to air pollution in the world’s most populous country in 2019.