Sri Lanka unveils $1BN relief plan as soaring food prices bite
Sri Lanka will increase pay and pensions for government employees, roll back some taxes on food and medicine and boost income support for the poorest citizens.

Sri Lanka unveiled a $1 billion relief package as President Gotabaya Rajapaksa’s government seeks to temper growing public anger over the surging prices of essential food and medical items in a country that’s running out of foreign exchange to pay for imports.
The government will raise civil servants salaries and pensions, remove some taxes on food and medicine and provide cash for its poorest citizens, a move critics say won’t help Sri Lanka’s state of finances and soaring inflation.
Keep reading
list of 4 itemsKey takeaways from Xi Jinping’s Europe trip
When will EVs become mainstream in the US?
Key takeaways from Xi Jinping’s European tour to France, Serbia and Hungary
The package accounts for 1.2% of gross domestic product, and will be re-allocated from the 3.9 trillion rupees budgeted to be spent in the whole of 2022, Rajapaksa’s brother and Finance Minister Basil Rajapaksa told a briefing in Colombo late Monday. There are no plans for new taxes, he added.
The relief covers about 2 million people who are on income support and is a clear signal the government is seeking to prevent a backlash over the the rising prices of wheat, sugar and milk power. Sri Lanka is struggling to purchase these key staples from abroad due to worsening foreign exchange shortages.
The escalating food prices also stem from domestic crop losses that have emerged after a government directive to stop chemical fertilizer use. The administration has included a plan to buy crops at higher-than-market rates from farmers who have been protesting for much of last year.
Sri Lanka’s main opposition slammed the relief package, saying it doesn’t address the issue of external liquidity and domestic inflation, which accelerated to 12.1% in December, the second-fastest pace in Asia after Pakistan.
“They are not addressing either of the problems. If they accommodate these wage increases by printing money inflation may go up further,” said Harsha de Silva, a lawmaker from the Samagi Jana Balawegara and former minister of economic reforms.
Emergency Support
Sri Lanka’s financial problems emerged with the start of the pandemic that has largely shuttered the tourism sector, a key source of foreign exchange earnings. In recent weeks, this has stoked debate among policymakers about whether it should seek a bailout from the International Monetary Fund or rely on bilateral emergency support from nations including China and India.
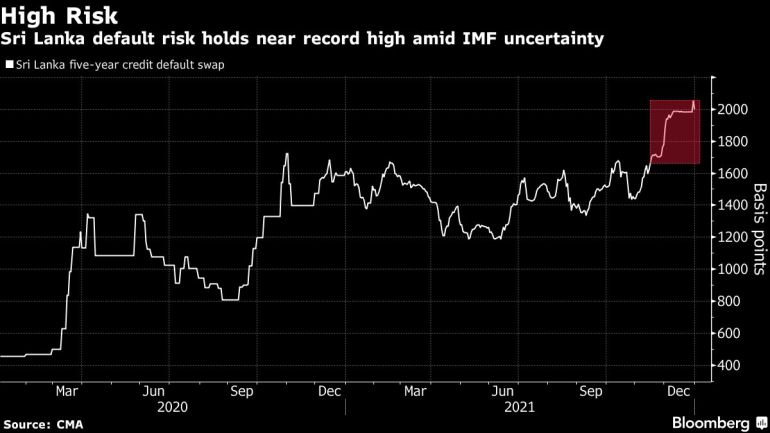
The country has $500 million of dollar bonds maturing Jan. 18 and another $1 billion in July. It has $3.1 billion of foreign exchange reserves, roughly enough to pay for two months of imports, based on extrapolations from previous government calculations.
Basil Rajapaksa said at Monday briefing that the government hasn’t made a decision on going to the IMF for support. In the past few weeks, Sri Lanka has held discussions with India for $1.9 billion in economic aid and used a $1.5 billion currency swap facility from China to build up its reserves.
Sri Lanka’s sovereign dollar bonds were mostly steady to higher on Tuesday. Notes due March 2020 were trading at 51.1 cents on the dollar, while those maturing in July 2022 were at 70.5 cents.